Book Recommendations (Goodbooks)
This tutorial demonstrates how to configure a recommendation engine using the Goodbooks-10k dataset. The dataset contains 6 million ratings for 10,000 popular books. This example uses the MongoDB connector; the same approach applies to other supported data stores.
Setup
Install required packages:
! pip install shaped
! pip install pyyaml
Initialize the CLI
Set your API key:
import os
SHAPED_API_KEY = os.getenv('TEST_SHAPED_API_KEY', '<YOUR_API_KEY>')
Initialize the CLI:
! shaped init --api-key $SHAPED_API_KEY
If you don't have an API key, see How to get an API key.
Data Preparation
Install dependencies
! pip install pandas
Download the dataset
Download and extract the dataset:
import zipfile
import os
def download_and_extract_dataset(url, destination_directory):
print(f"Downloading dataset from {url}...")
os.makedirs(destination_directory, exist_ok=True)
zip_file_path = os.path.join(destination_directory, os.path.basename(url))
# Download the ZIP file
!wget $url --no-check-certificate -P $destination_directory
# Extract the contents of the ZIP file
with zipfile.ZipFile(zip_file_path, 'r') as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall(destination_directory)
# Directory name for storing datasets
DIR_NAME = "notebook_assets"
# Download and extract each dataset
datasets = [
("https://github.com/zygmuntz/goodbooks-10k/releases/download/v1.0/ratings.zip", DIR_NAME),
("https://github.com/zygmuntz/goodbooks-10k/releases/download/v1.0/books.zip", DIR_NAME)
]
for dataset_url, destination_dir in datasets:
download_and_extract_dataset(dataset_url, destination_dir)
Inspect the data:
import pandas as pd
data_dir = "notebook_assets"
events_df = pd.read_csv(f'{data_dir}/ratings.csv')
books_df = pd.read_csv(f'{data_dir}/books.csv')
display(events_df.head())
display(books_df.head())
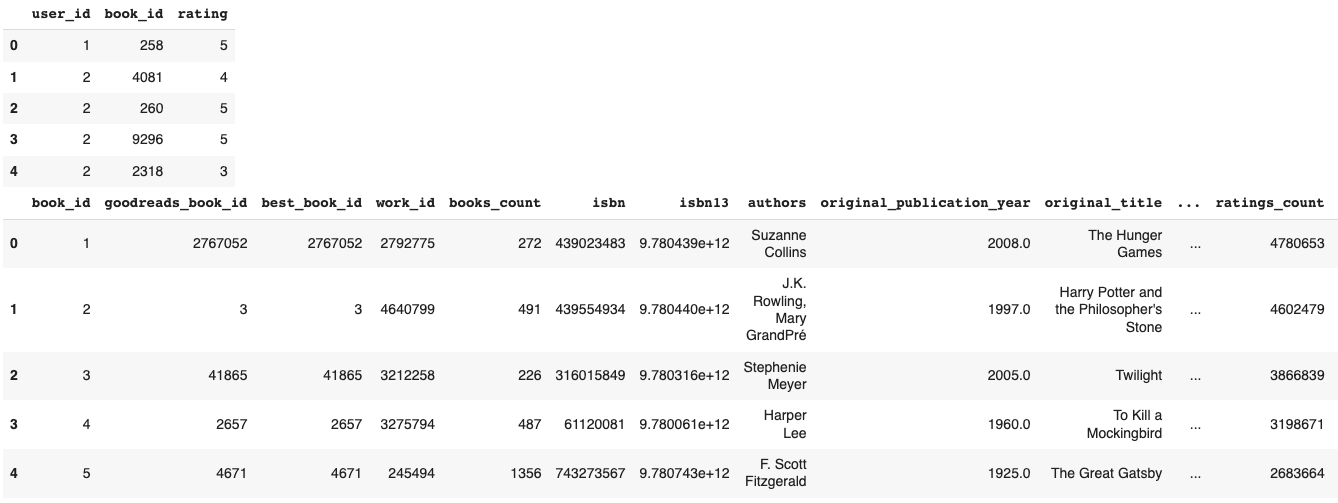
Required columns
The minimum required columns for an interaction table are:
user_id: User identifieritem_id: Item identifierlabel: Interaction labelcreated_at: Timestamp
The ratings data contains:
user_id: Reader identifier (1 to 53424)book_id: Book identifier (1 to 10000), used asitem_idrating: Rating value (1 to 5)
The dataset lacks a created_at column. Since ratings are sorted by time, create a timestamp column:
events_df = events_df[["user_id","book_id","rating"]]
events_df = events_df.head(1000)
# Create a new column 'created_at' with ascending values
events_df['created_at'] = range(1, len(events_df) + 1)
display(events_df.head())
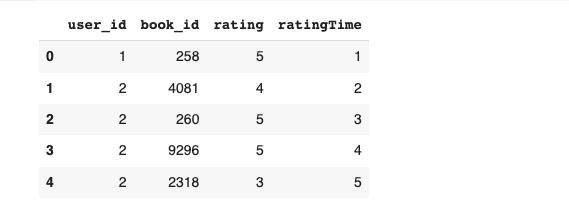
Create table using MongoDB connector
This example uses the MongoDB connector to upload local CSV files. Steps:
- Set up a MongoDB instance and obtain a connection string. See MongoDB connection string documentation.
- Create a database and collection (this example uses "goodbooks" database and "ratings" collection).
- Define the table schema in YAML.
- Create the table and insert data.
Define the table schema:
"""
Create a Shaped Table schema and store in a .yaml file.
"""
import yaml
dir_path = "notebook_assets"
events_table_schema = {
"name": "goodbooks_events",
"schema_type": "MONGODB",
"schedule_interval": "@daily",
"mongodb_connection_string": "<YOUR_CONNECTION_STRING>",
"database": "goodbooks",
"collection": "ratings"
}
with open(f'{dir_path}/events_table_schema.yaml', 'w') as file:
yaml.dump(events_table_schema, file)
Create the table:
! shaped create-table --file $DIR_NAME/events_table_schema.yaml
Check table status:
! shaped list-tables
Response:
tables:
- table_name: goodbooks_events table_uri: https://api.shaped.ai/v2/tables/goodbooks_events created_at: 2023-09-08T12:35:12 UTC schema_type: MONGODB status: ACTIVE
Insert data:
! shaped table-insert --table-name goodbooks_events --file $DIR_NAME/ratings.csv --type 'csv'
Create the engine
This example uses ratings to build a collaborative filtering engine. Higher ratings indicate stronger user preference.
Define the engine schema:
"""
Create a Shaped Engine schema and store in a .yaml file.
"""
import yaml
goodbooks_ratings_engine_schema = {
"data": {
"interaction_table": {
"name": "goodbooks_events",
"type": "query",
"query": "SELECT JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.book_id') as item_id, JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.rating') as label, JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.ratingTime') as created_at, JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.user_id') as user_id FROM goodbooks_events"
}
},
"training": {
"models": [
{
"name": "als",
"policy_type": "als"
}
]
}
}
dir_path = "notebook_assets"
with open(f'{dir_path}/goodbooks_ratings_engine_schema.yaml', 'w') as file:
yaml.dump(goodbooks_ratings_engine_schema, file)
Create the engine:
"""
Create a Shaped Engine using the .yaml schema file.
"""
! shaped create-engine --file $DIR_NAME/goodbooks_ratings_engine_schema.yaml
Response:
{
"data": {
"interaction_table": {
"name": "goodbooks_events",
"type": "query",
"query": "SELECT JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.book_id') as item_id, JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.rating') as label, JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.ratingTime') as created_at, JSON_EXTRACT_STRING(document, '$.user_id') as user_id FROM goodbooks_events"
}
},
"training": {
"models": [
{
"name": "als",
"policy_type": "als"
}
]
}
}
engine_url: https://api.shaped.ai/v2/engines/goodbooks_book_recommendations
Monitor engine status
Engine creation and training can take up to several hours, depending on data volume and attributes. For this example, training typically completes within 30 minutes.
Check status:
! shaped list-engines
Response:
engines:
- engine_name: goodbooks_book_recommendations engine_uri: https://api.shaped.ai/v2/engines/goodbooks_book_recommendations created_at: 2023-09-12T01:46:21 UTC status: SCHEDULING
The engine progresses through these stages:
SCHEDULINGFETCHINGTRAININGDEPLOYINGACTIVE
Once the status is ACTIVE, the engine is ready for queries.
Query recommendations
Query recommendations using the Query endpoint. Provide a user_id and the number of results to return. Ensure the user_id exists in the table.
Using the CLI:
! shaped query --engine-name goodbooks_book_recommendations \
--query "SELECT * FROM similarity(embedding_ref='als', limit=50, encoder='precomputed_user', input_user_id='\$user_id') LIMIT 5" \
--parameters '{"user_id": "5"}'
Response:
{
"results": [
{
"id": "8",
"score": 1.0
},
{
"id": "27",
"score": 0.90909091
},
{
"id": "101",
"score": 0.90909091
},
{
"id": "24",
"score": 0.90909091
},
{
"id": "2",
"score": 0.81818182
}
]
}
The response contains an array of result objects with book IDs and scores.
Using the REST API:
! curl https://api.shaped.ai/v2/engines/goodbooks_book_recommendations/query \
-H "x-api-key: <YOUR_API_KEY>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query": "SELECT * FROM similarity(embedding_ref=''als'', limit=50, encoder=''precomputed_user'', input_user_id=''$user_id'') LIMIT 5",
"parameters": {
"user_id": "5"
}
}'
Clean up
Delete tables, engines, and associated assets when finished:
! shaped delete-table --table-name goodbooks_events
! shaped delete-engine --engine-name goodbooks_book_recommendations
! rm -r notebook_assets
Response:
message: Table with name 'goodbooks_events' was successfully deleted
message: Engine with name 'goodbooks_book_recommendations' is deleting...